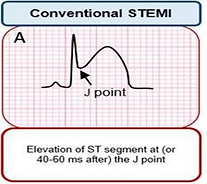
Conventional STEMI
STEMI is defined by the ESC/ACCF/AHA/WHF Task Force for the Universal Definition of Myocardial Infarction as:
-
New ST Elevation at the J point in V2-3 of at least two contiguous leads
-
≥2mm in men
-
≥1.5mm in women
-
-
New ST Elevation in the J point of at least 1mm in two contiguous leads (except for V2-3)

STEMI Equivalents
-
Chest Pain with New Onset Left Bundle Branch Block (LBBB)
-
Posterior MI
-
Sgarbossa Criteria
New Onset LBBB
-
QRS prolongation >120 ms
-
Abnormally appearing QRS complex
-
Leads V1-V3 will have deep S waves
-
Leads V5-V6 will have tall R waves


Posterior STEMI
-
ST Depression >0.05 mV in V1-V3
-
Tall R in V1/V2 with R/S ratio >1 in V2
-
ST Elevation in Leads V7-V9 (Posterior Leads)
Sgarbossa's Criteria

Sgarbossa criteria used to diagnose a STEMI in the context of LBBB on ECG. In the past, a new LBBB in a patient with ischemic chest pain was considered to be an indication for a patient to undergo cardiac catheterization. However, in recent years this has become more controversial with evidence suggesting these patients may be managed more conservatively
High Risk ECGs
-
Wellen's Sign
-
DeWinter's Sign
-
Hyperacute T-wave
-
Dynamic ST Changes
-
Diffuse ST Depressions with ST Elevation in aVR
Wellen's Sign

DeWinter's Sign

De Winter’s sign:
-
Sign of an occlusion of the left anterior descending artery
-
Upsloping ST depression greater than 1mm in the precordial leads
-
Prominent, tall, and symmetrical T waves in the precoridal leads
-
Absence of ST elevation in the precordial leads
-
Reciprocal ST elevation of 0.5mm-1mm in AVR
Hyperacute T-wave

Diffuse ST Depressions with ST Elevation in aVR

Other Noteworthy ECGs
Pericarditis

ECG changes suggestive of Pericarditis:
-
Diffuse ST-segment elevations
-
PR depressions, best seen in II and V6
-
ST Depression in lead AVR with PR elevation
Acute Pulmonary Embolism

ECG changes suggestive of P.E.:
-
Sinus tachycardia
-
S1Q3T3 pattern
-
T wave inversion in V1–V4
-
RBBB
Cardiac Tamponade

ECG changes suggestive of Tamponade.:
-
Low voltage QRS
-
Electrical alternans
-
Nonspecific ST-T changes
